
연구
Research Outcome
미래를 창조하는 포스텍 화학공학과
Prussian Blue Analog as a Functional Additive for Restoring Sulfide Solid Electrolytes: Enhancing Moisture Stability in All-Solid-State Batteries
- Title of paper
- Prussian Blue Analog as a Functional Additive for Restoring Sulfide Solid Electrolytes: Enhancing Moisture Stability in All-Solid-State Batteries
- Author
- [조창신 교수 연구실] 황화물 고체 전해질 복원을 위한 기능성 첨가제로서의 프러시안 블루 아날로그
- Publication in journal
- Advanced Materials
- Publication date
- 20251021
Abstract
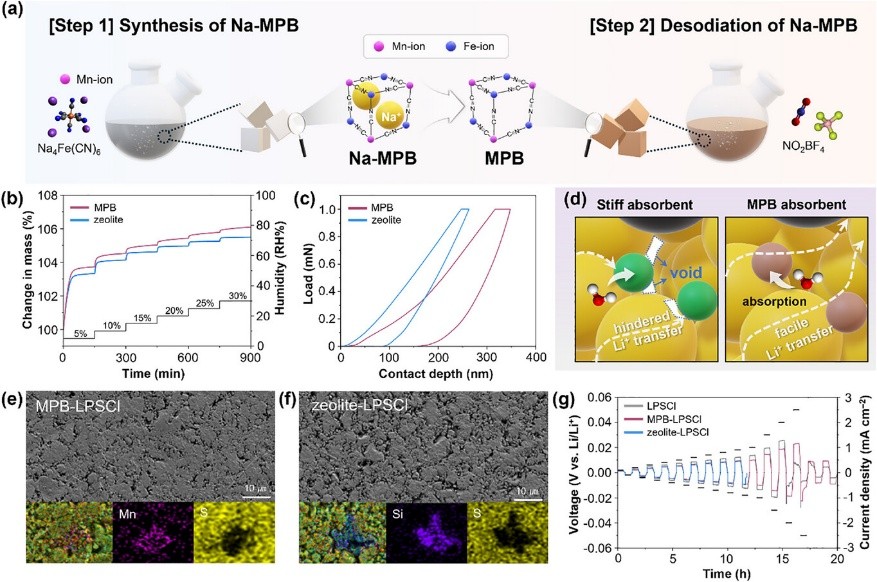
Sulfide-based solid-state electrolytes (SSEs) hold significant potential for all-solid-state batteries (ASSBs), but their severe degradation upon exposure to moisture remains a major barrier to their practical application. In this work, Prussian blue analogs (PBAs) are introduced as functional additives into the SSEs to enhance moisture stability. It is demonstrated that PBAs can not only suppress moisture-induced degradation of SSEs but also actively reverse it, offering a reviving function that restores the electrochemical performance of previously degraded SSEs. When PBAs are simply postmixed with previously degraded SSEs under 5% relative humidity for 6 h, the resulting cells exhibited an average Coulombic efficiency of 99.9% over 500 cycles with 95.2% capacity retention. This restoring behavior is attributed to the open-framework structure of PBAs, which provides abundant interstitial and coordination sites that facilitate the efficient absorption of hydrated water molecules and evolved gases such as H2S. In addition, PBAs exhibit a ductile nature that mitigates the increase in interfacial resistance typically induced by conventional additives, thereby preserving high ionic conductivity of SSEs. These results highlight PBAs as next-generation multifunctional additives―capable of both protecting and recovering sulfide SSEs, offering a viable route toward stable and durable sulfide-based ASSBs assembled under ambient conditions.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202516613
Link: https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202516613



