연구
Research Outcome
미래를 창조하는 포스텍 화학공학과
Solvent-Induced Octahedral Self-Assembly of Prussian Blue and Its Applications in Sodium-Ion Capacitors
- Title of paper
- Solvent-Induced Octahedral Self-Assembly of Prussian Blue and Its Applications in Sodium-Ion Capacitors
- Author
- [조창신 교수 연구실] 용매 유도 팔면체 프러시안 블루의 자기 조립 및 나트륨 이온 커패시터에서의 응용
- Publication in journal
- Advanced Functional Materials
- Publication date
- 20250723
Abstract
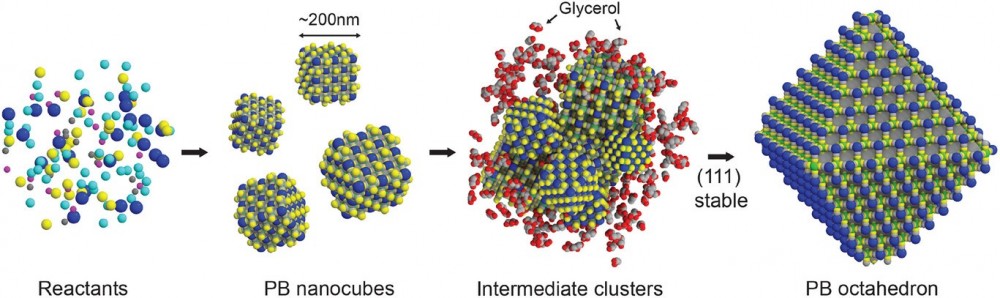
Controlling the morphology and exposed facets of nano/microparticles is crucial for enhancing material properties in electrochemical reactions, photoreactions, and biosensors. However, Prussian Blue (PB), a type of metal–organic framework (MOF), rapidly and stably forms a cubic structure, making shape control difficult and leaving its formation process unclear. Here, the octahedral formation of PB particles in glycerol is discovered, which differs from the cubic particles formed in water. Glycerol slows down the crystallization-growth process of PB, allowing direct observation of a stepwise growth in which cubic seeds initially form and subsequently self-assemble into octahedra. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation suggests that glycerol molecules stabilize the (111) surfaces of PB crystals over the (100) planes, inducing the self-assembly of PB particles into an octahedral shape. It is also observed that the water-to-glycerol ratio influences PB's surface charge and affects the assembly behavior of PB crystals, resulting in the formation of isolated nanocubes (edge length ≈200 nm), microcubes (edge length ≈1 µm), and octahedra (edge length ≈1 µm). As an active material for sodium-ion capacitors, octahedron-shaped PB, with its significantly higher surface area, exhibits outstanding cycling performance, surpassing cubic PB.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202508095
Link: https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adfm.202508095