
연구
Research Outcome
미래를 창조하는 포스텍 화학공학과
Low-Surface-Energy Capped Hydrogel Micropillar Arrays for Transparent Superhydrophobic Antifogging Surfaces
- Title of paper
- Low-Surface-Energy Capped Hydrogel Micropillar Arrays for Transparent Superhydrophobic Antifogging Surfaces
- Author
- [이효민교수님 연구실] 초소수성 김 서림 방지 표면 개발
- Publication in journal
- Small
- Publication date
- 20251022
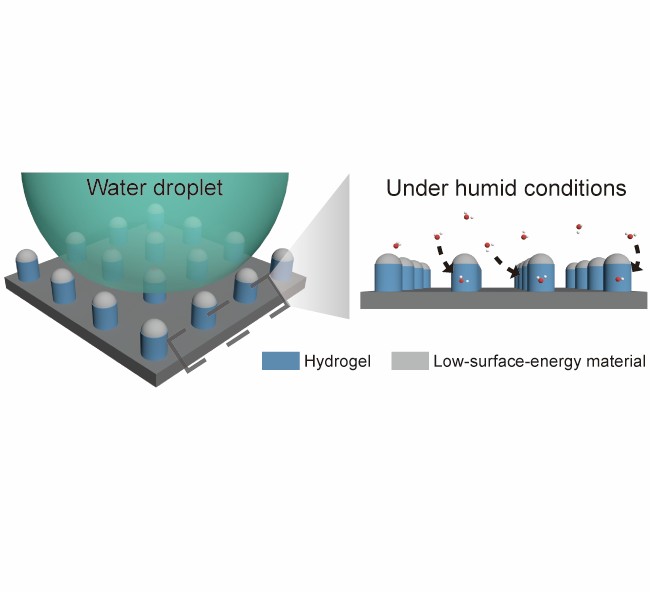
[Abstract]
Transparent substrates widely used in applications such as optical displays, solar cells, and medical devices are highly susceptible to fogging and contamination, often degrading their visual clarity. While various antifogging approaches have been explored, achieving sustained transparency across diverse environments through a simple and scalable design remains a critical challenge in surface engineering. Herein, a structurally simple, low-surface-energy polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) capped hydrogel micropillar arrays comprising poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) are introduced to achieve transparent superhydrophobic antifogging surfaces. The exposed sidewalls of hydrogel micropillars effectively absorb water vapor, while the low-surface-energy caps on the top offer superhydrophobicity with a high water contact angle (>160°). It is demonstrated that this design effectively prevents fogging and exhibits self-cleaning properties to maintain high optical transparency (>84%), offering a scalable and effective solution for transparent substrates operating in diverse optical and environmental applications.
LINK: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smll.202509390



