
연구
Research Outcome
미래를 창조하는 포스텍 화학공학과
Development of a Femtosensitive Electrochemical Aptasensor for Tuberculosis Ag85B Detection
- Title of paper
- Development of a Femtosensitive Electrochemical Aptasensor for Tuberculosis Ag85B Detection
- Author
- [이정욱 교수 연구실] 결핵 바이오마커 Ag85B의 초고감도·특이적 검출을 위한 전기화학 압타센서 개발
- Publication in journal
- Analytical Chemistry, 97.29: 15798-15807, 2025
- Publication date
- 20250711
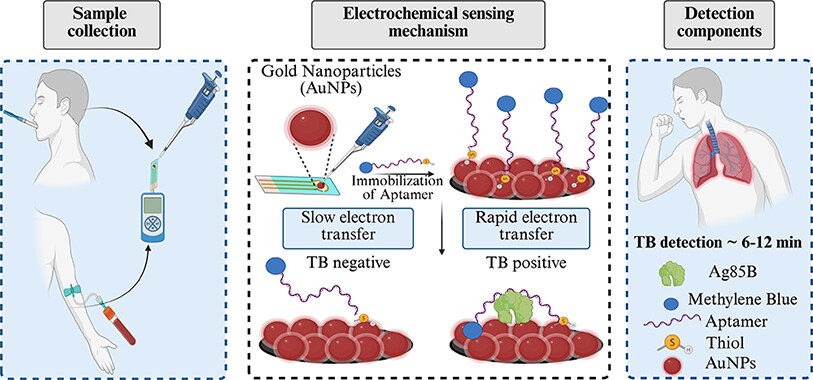
[Abstract]
Tuberculosis (TB) disease continues to pose a major global health challenge, particularly in resource-limited settings where access to rapid, sensitive, and affordable diagnostic tools remains limited. Traditional methods, such as sputum smear microscopy and culture techniques, are time-consuming, lack sensitivity, and often require well-equipped laboratories, making them unsuitable for rapid, point-of-care diagnostics. To address these challenges, developing a rapid, sensitive, and selective biosensor is essential for the early detection of TB. Aptamer-based biosensors offer a promising approach for sensitive and specific detection of disease biomarkers. In this study, an electrochemical aptasensor tailored for precisely detecting the tuberculosis biomarker Antigen 85B (Ag85B) was developed. A diverse library of random oligonucleotide sequences was initially screened to identify aptamers with high binding affinity for Ag85B. The aptamer selection process involved immobilizing Ag85B on polyvinylidene fluoride membranes through aldehyde surface modifications, followed by incubation with the DNA library mixture. Aptamers with high specificity for Ag85B were isolated based on iterative selection and amplification. The selected aptamers were then integrated into a biosensor by immobilization on gold nanoparticle-modified screen-printed carbon electrodes using thiol-gold chemistry. The performance of the aptasensor was enhanced by adjusting key parameters such as aptamer concentration and incubation time, resulting in a detection limit of 0.2 fM. The resulting biosensor demonstrated remarkable selectivity for Ag85B and exhibited robust stability across multiple uses and extended storage, making it a promising tool for rapid and reliable TB diagnosis.



