
연구
Research Outcome
미래를 창조하는 포스텍 화학공학과
Rational Design of Biocompatible Ir(III) Photosensitizer to Overcome Drug-Resistant Cancer via Oxidative Autophagy Inhibition
- Title of paper
- Rational Design of Biocompatible Ir(III) Photosensitizer to Overcome Drug-Resistant Cancer via Oxidative Autophagy Inhibition
- Author
- [박태호교수 연구실] 약물 저항성 암 극복을 위한 산화적 자가포식을 억제하는 생체적합성 Ir(III) 광감작제의 합리적 설계
- Publication in journal
- Advanced Science
- Publication date
- 20250113
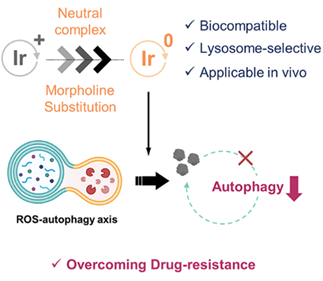
Abstract
Autophagy is a crucial quality control mechanism that degrades damaged cellular components through lysosomal fusion with autophagosomes. However, elevated autophagy levels can promote drug resistance in cancer cells, enhancing their survival. Downregulation of autophagy through oxidative stress is a clinically promising strategy to counteract drug resistance, yet precise control of oxidative stress in autophagic proteins remains challenging. Here, a molecular design strategy of biocompatible neutral Ir(III) photosensitizers is demonstrated, B2 and B4, for precise reactive oxygen species (ROS) control at lysosomes to inhibit autophagy. The underlying molecular mechanisms for the biocompatibility and lysosome selectivity of Ir(III) complexes are explored by comparing B2 with the cationic or the non-lysosome-targeting analogs. Also, the biological mechanisms for autophagy inhibition via lysosomal oxidation are explored. Proteome analyses reveal significant oxidation of proteins essential for autophagy, including lysosomal and fusion-mediator proteins. These findings are verified in vitro, using mass spectrometry, live cell imaging, and a model SNARE complex. The anti-tumor efficacy of the precise lysosomal oxidation strategy is further validated in vivo with B4, engineered for red light absorbance. This study is expected to inspire the therapeutic use of spatiotemporal ROS control for sophisticated modulation of autophagy.
Doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202407236
Link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.202407236



