연구
Research Outcome
미래를 창조하는 포스텍 화학공학과
Enhanced production of Dopa‐incorporated mussel adhesive protein using engineered translational machineries
- Title of paper
- Enhanced production of Dopa‐incorporated mussel adhesive protein using engineered translational machineries
- Author
- [차형준교수 연구실]단백질 번역기계의 엔지니어링을 통한 Dopa 도입된 단백질 생산 증대
- Publication in journal
- Biotechnology & Bioengineering 117(7), p1961-1969, 2020
- Publication date
- 20200615
[Abstract]
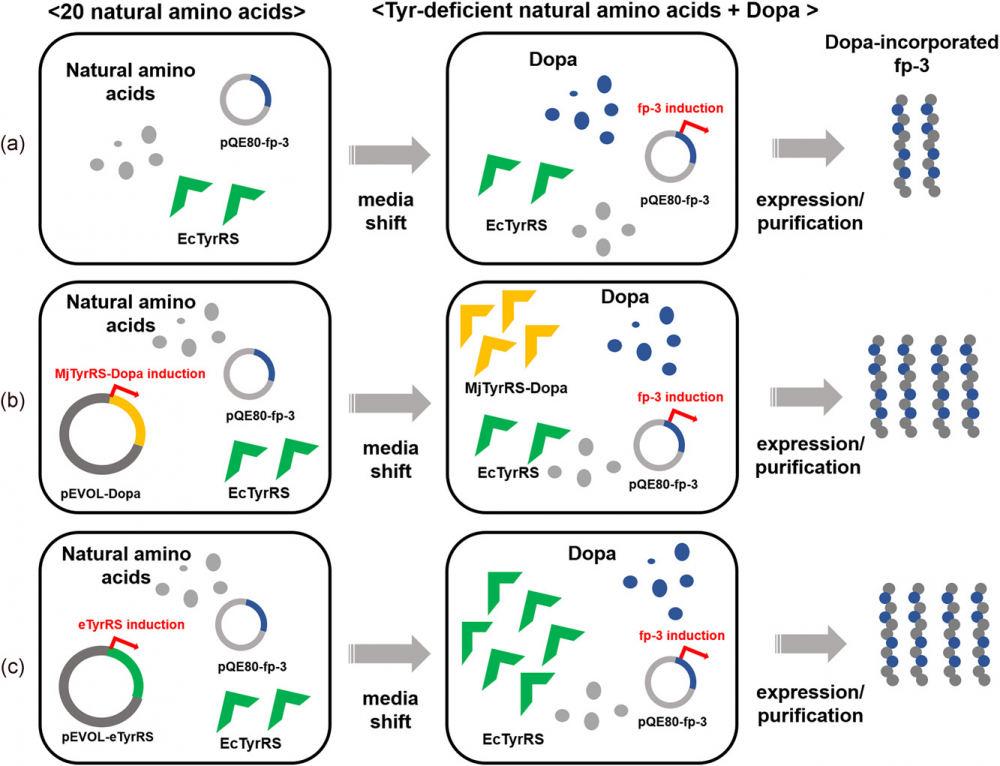
Mussel adhesive proteins (MAPs) have great potential as bioglues, particularly in wet conditions. Although in vivo residue‐specific incorporation of 3,4‐dihydroxyphenylalanine (Dopa) in tyrosine‐auxotrophic Escherichia coli cells allows for production of Dopa‐incorporated bioengineered MAPs (d MAPs), the low production yield hinders the practical application of d MAPs. This low production yield of d MAPs is due to low translational activity of a noncanonical amino acid, Dopa, in E. coli cells. Herein, to enhance the production yield of d MAPs, we investigated the coexpression of Dopa‐recognizing tyrosyl‐tRNA synthetases (TyrRSs). To use the Dopa‐specific Methanococcus jannaschii TyrRS (MjTyrRS‐Dopa), we altered the anticodon of tyrosyl‐tRNA amber suppressor into AUA (MjtRNATyrAUA) to recognize a tyrosine codon (AUA). Co‐overexpression of MjTyrRS‐Dopa and MjtRNATyrAUA increased the production yield of Dopa‐incorporated MAP foot protein type 3 (d fp‐3) by 57%. Similarly, overexpression of E. coli TyrRS (EcTyrRS) led to a 72% higher production yield of d fp‐3. Even with coexpression of Dopa‐recognizing TyrRSs, d fp‐3 has a high Dopa incorporation yield (over 90%) compared to ones prepared without TyrRS coexpression.
DOI: 10.1002/bit.27339
LINK: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/bit.27339