
연구
Research Outcome
미래를 창조하는 포스텍 화학공학과
Structural Modification Effect of Se-doped Porous Carbon for Hydrogen Evolution Coupled Selective Electrooxidation of Ethylene Glycol to Value-added Glycolic Acid
- Title of paper
- Structural Modification Effect of Se-doped Porous Carbon for Hydrogen Evolution Coupled Selective Electrooxidation of Ethylene Glycol to Value-added Glycolic Acid
- Author
- : [김원배 교수님 연구실] 그린수소 및 고부가 화합물 동시생산을 위한 셀레늄 도핑 다공성 탄소계 전기화학촉매 연구
- Publication in journal
- Small 2024, 20, 2404540
- Publication date
- 20240909
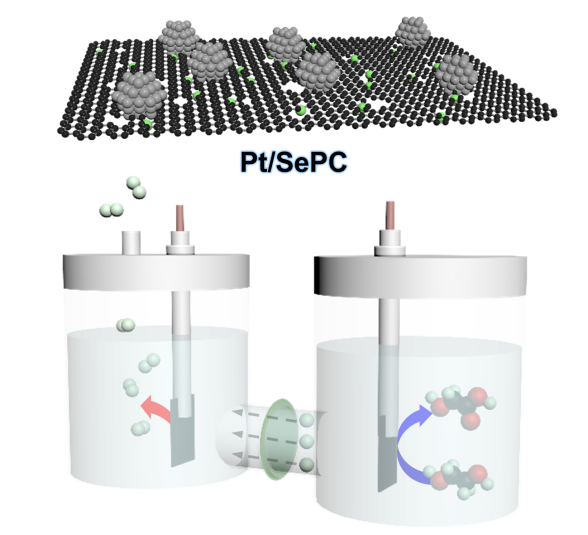
[Abstract]
The ethylene glycol oxidation reaction (EGOR) has attracted attention because ethylene glycol (EG), which exhibits large-scale production and a low market price, can be reformed into valuable glycolic acid (GCA) with the cogeneration of high-purity hydrogen gas during the reaction. In this study, a noble catalyst material of Pt nanoparticles supported on Se-doped porous carbon (Pt/SePC) is prepared and investigated for the selective electrochemical oxidation of EG to GCA. Pt/SePC achieved a maximum EG conversion of 94.6% and GCA selectivity of 84.4% and maintained this high performance with negligible degradation during durability tests. Furthermore, the EGOR required lower overpotential rather than the oxygen evolution reaction, thus the EGOR coupled with the hydrogen evolution reaction can reduce the cell overpotential to 0.60 V, which is much lower than that of water electrolysis (1.58 V). The effect of Se doping is investigated through experimental analyses and density functional theory (DFT) calculations, and they show that Se modified the binding energy of Pt nanoparticles and the adsorption energy of reactants by lattice deformation and charge density modification. This study provides scientific insights and strategies for electrocatalyst design for the selective oxidation of polyols to value-added chemicals via the cogeneration of hydrogen gas.



