연구
Research Outcome
미래를 창조하는 포스텍 화학공학과
Design of Highly Selective and Sensitive Optical Sensor for Arsenic(III) based on the Orientational Coupling between L-cysteine and Liquid Crystals
- Title of paper
- Design of Highly Selective and Sensitive Optical Sensor for Arsenic(III) based on the Orientational Coupling between L-cysteine and Liquid Crystals
- Author
- [김영기 교수 연구실] L-시스테인과 액정 간의 배향 결합을 기반으로 한 비소(III)에 대해 고선택성 및 고민감도를 가지는 광학 센서 설계
- Publication in journal
- Advanced Optical Materials 2403136 (2025)
- Publication date
- 20250124
Abstract
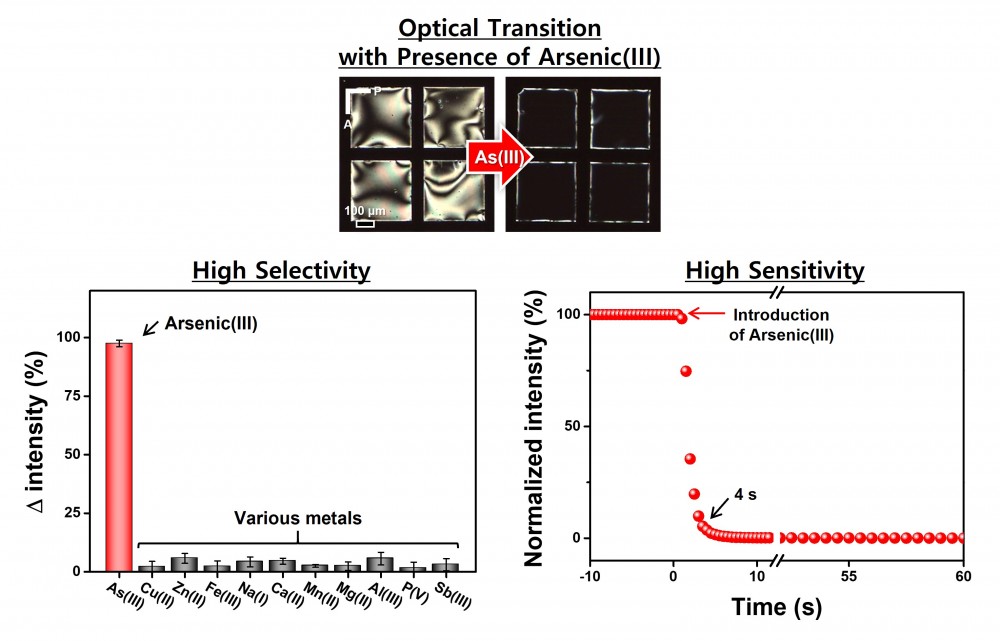
Water pollution by toxic arsenic compounds, As(III), has emerged as a global problem, because prolonged exposure causes serious health issues. Accordingly, it is critical to monitor As(III) in drinking water and food, but conventional techniques still require complex and costly instruments that are not affordable in third-world countries where As(III) contamination is significant. To resolve this social issue, simple and generalizable principles for the design of As(III) sensors are proposed by integrating the selective binding of L-cysteine (L-cys) with As(III) into the unique ability of liquid crystals (LCs) to transduce stimuli into macroscopic optical signals. We revealed significant orientational coupling of L-cys with LCs that can be modulated by the selective binding of L-cys with As(III) at the LC-aqueous interface. When decorated with both L-cys and surfactants, the LC-aqueous interface is subjected to competition between the L-cys-imposed tangential (bright state) and surfactant-imposed homeotropic (dark state) anchoring of LCs. Consequently, the competitive intermolecular interactions offers the basis for a highly stable and versatile LC material that can selectively detect As(III) in water and also quantify its concentration from trace to high levels (1 ppb – 4 ppm) via distinct optical outputs within 2 min.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202403136
Link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adom.202403136