
연구
Research Outcome
미래를 창조하는 포스텍 화학공학과
Poly[Bis(4-Phenyl)(2,4,6-Trimethylphenyl)Amine] in Perovskite Solar Cells: Advances via Molecular Engineering
- Title of paper
- Poly[Bis(4-Phenyl)(2,4,6-Trimethylphenyl)Amine] in Perovskite Solar Cells: Advances via Molecular Engineering
- Author
- [박태호 교수 연구실]_3차 아민 기반 정공 전달 고분자의 분자 공학 전략 탐구
- Publication in journal
- Sol. RRL2024, 2400048
- Publication date
- 20240325
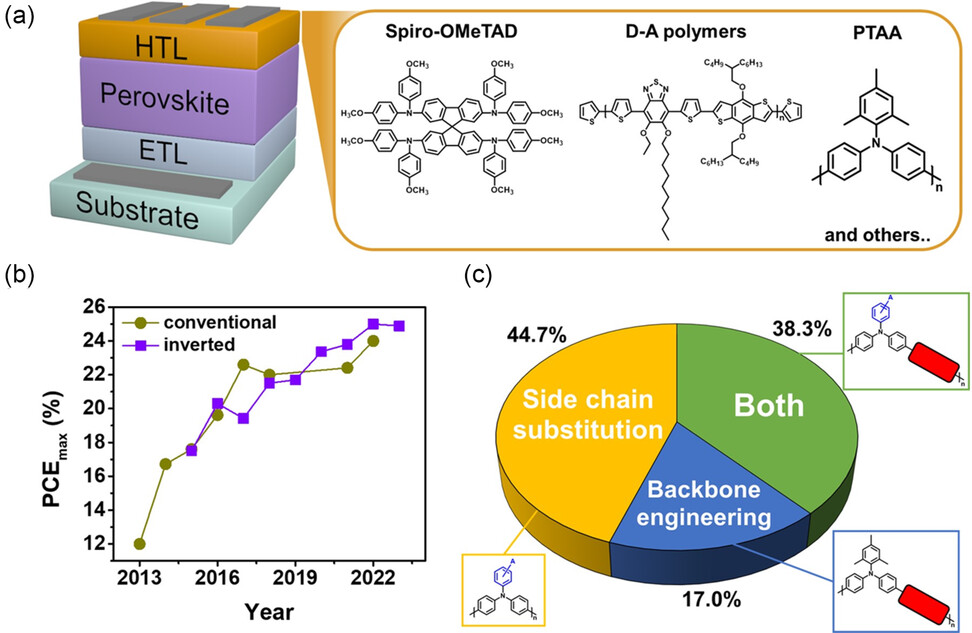
[Abstract]
To improve the performance of perovskite solar cells (PSCs), studying the materials that constitute each layer of the device is important. Among the commonly used materials in the hole-transport layer (HTL), poly[bis(4-phenyl)(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)amine] (PTAA) stands out as one of the most employed. This hole-transport material (HTM) offers many advantages, including thin-film fabricating feasibility, ease of synthesis, and sufficient energy levels. Further, PSCs employing PTAA as the HTL exhibit a high-power conversion efficiency. However, it has some drawbacks, including low crystallinity and poor device stability. To overcome these limitations, extensive studies focusing on improving its properties by molecular engineering have been conducted. In this review, the strategies for engineering the molecular structures of triaryl amine polymers are introduced. The strategies are classified into three groups: backbone engineering, side-chain substitution, and a combination of both. Furthermore, future directions for achieving HTMs with various properties for high-performance PSCs are suggested.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/solr.202400048
Link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/solr.202400048



